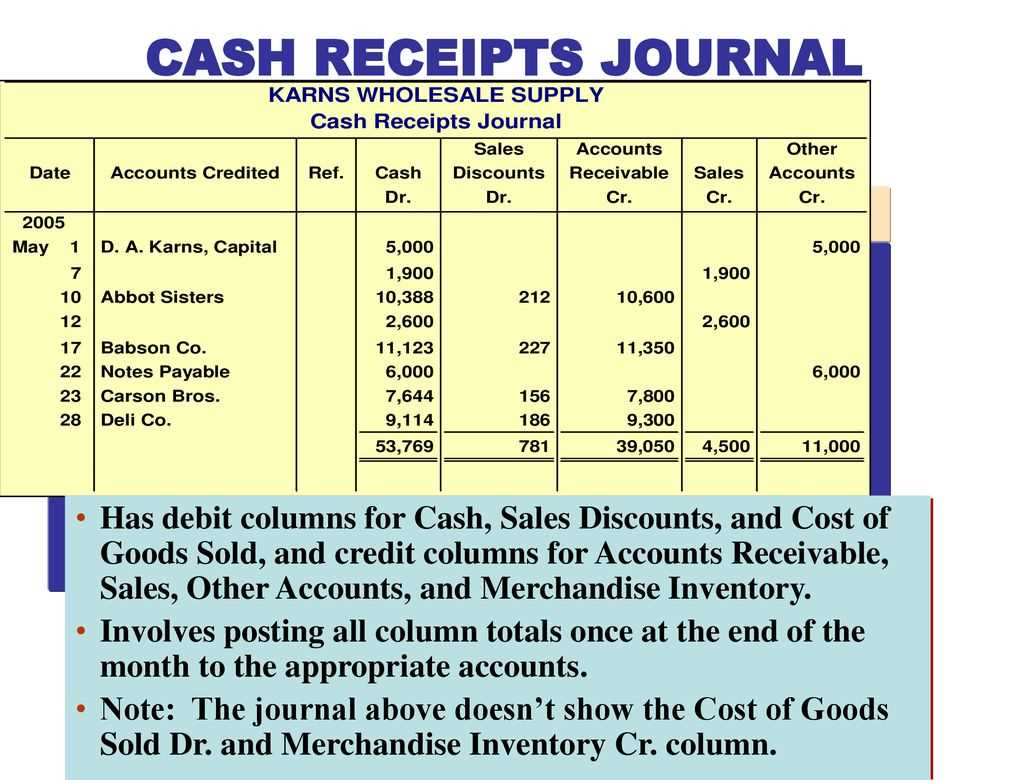
Use a structured sales and cash receipts journal template to simplify tracking and reporting financial transactions. This template ensures all sales and cash receipts are accurately recorded, making it easier to monitor cash flow and manage accounts.
Keep columns organized to clearly separate each transaction. Include essential details like date, description, sales amount, and cash received. By maintaining this structure, you can avoid confusion and streamline the bookkeeping process.
Regular updates to your journal are necessary. Enter sales and cash receipts as they happen to avoid missing any entries. This will provide a real-time snapshot of your business’s financial status, aiding in decision-making and future planning.
Here is a revised article outline where repetitive terms have been minimized, maintaining the original meaning:
Start by categorizing sales and cash receipts to ensure clarity in tracking. This process streamlines entries, allowing for easy identification and correction of errors. Group transactions into logical sections, such as sales on credit, cash sales, and customer payments. This approach helps in quickly accessing relevant information without unnecessary confusion.
Next, focus on maintaining an accurate and simple format. Keep column headers clear and concise, using terms that describe the transaction’s nature, such as ‘Date’, ‘Account’, ‘Amount’, and ‘Description’. Avoid overcomplicating with excess data that does not directly impact daily operations. A streamlined format ensures faster entries and reduces mistakes during recording.
Lastly, ensure regular updates. Promptly enter sales and receipts to avoid backlog. Timely updates prevent errors that might arise from delayed entries and provide an up-to-date financial snapshot. Regular checks guarantee the accuracy of the data and improve the reliability of financial statements.
Here’s a detailed article plan on “Sales and Cash Receipts Journal Template” in HTML format, with six practical and specific headings:
Begin by identifying the key sections that should be included in a sales and cash receipts journal template. Each of these sections will guide users to accurately record transactions, track payments, and understand their financial position. Below are six practical headings that will form the structure of the template:
1. Sales Transactions: Capturing Key Details
Focus on the essential information needed to record each sale. Include fields for transaction date, customer name, item or service sold, amount, and applicable tax. Ensure all amounts are recorded clearly, distinguishing between gross sales and taxable amounts.
2. Cash Payments: Recording Incoming Funds
Dedicate a section specifically for cash receipts, including payments received via cash, check, or electronic transfer. Include details such as the payment method, date received, payer’s name, and the total amount. This section helps track incoming funds and ensures that all receipts are logged accurately.
3. Receipt Numbering System: Ensuring Orderly Tracking
Implement a structured numbering system for each receipt or sale entry. This will provide easy cross-referencing in case of future audits or inquiries. Maintain consistency in the numbering to avoid confusion between different records.
4. Sales Returns and Adjustments
Allow space for entries related to returns or adjustments. Clearly separate these from standard sales, and make sure they reflect the corrected amounts. Specify whether the return is due to product defects, customer dissatisfaction, or other reasons, and adjust the overall sales totals accordingly.
5. Balancing the Journal: Cross-Checking Data
Include a reconciliation section where users can compare total sales and receipts with their records in other accounting systems. This is an important step to ensure that the journal matches bank deposits and cash on hand.
6. Summary and Reporting: Quick Financial Insights
Provide space for summarizing the daily, weekly, or monthly totals. This section can include total sales, total cash receipts, and any adjustments. By reviewing this summary regularly, users can gain insights into cash flow and overall business performance.
- Sales and Cash Receipts Journal Template
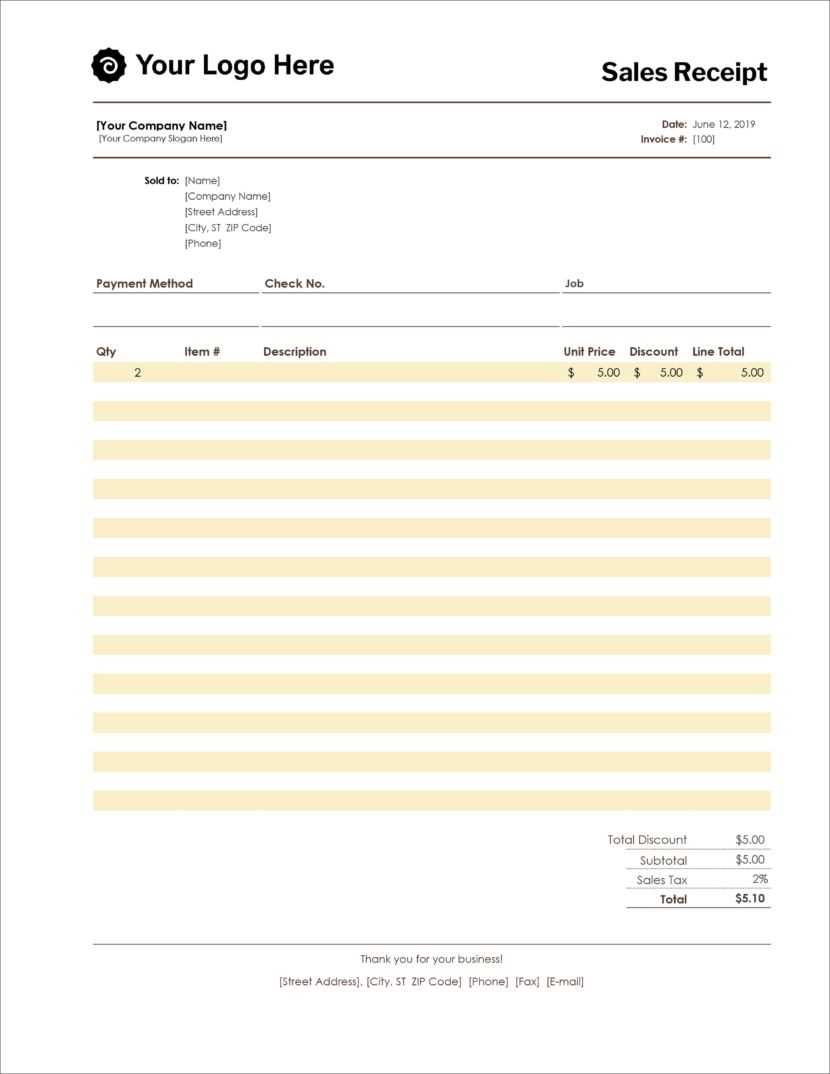
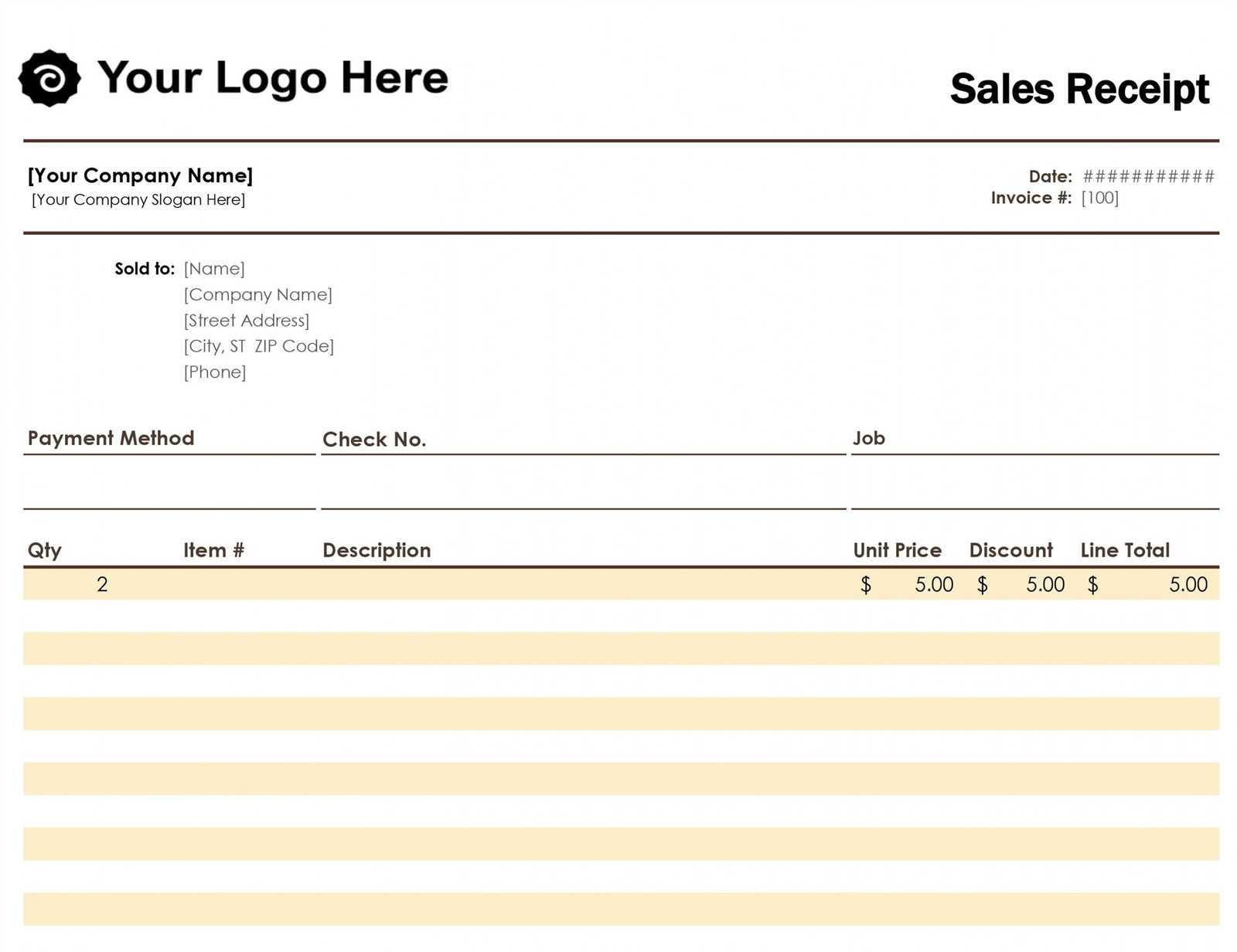
Begin with a simple structure that includes columns for the date, description, invoice number, amount received, and payment method. The journal should allow you to clearly track each sale and cash receipt for easy reconciliation at the end of the month or financial period.
Key Components of the Template
Each entry in the sales and cash receipts journal should have the following components:
- Date: The date the sale or cash receipt occurred.
- Description: A brief summary of the transaction (e.g., “Sale of goods” or “Payment received for invoice #12345”).
- Invoice Number: Include the related invoice number for reference when applicable.
- Amount Received: The total amount of cash or check received, or the total payment processed.
- Payment Method: Specify the payment method (e.g., “Cash”, “Credit Card”, “Bank Transfer”).
How to Use the Template Effectively
Ensure you update the journal daily, capturing every transaction as it happens. This will maintain accuracy and reduce errors. Regularly reconcile the totals with bank statements or cash flow reports to identify any discrepancies.
Begin by selecting a software tool or template to structure the sales journal. Ensure that it includes key columns like the transaction date, customer name, invoice number, sales amount, tax amount, and total amount due. If using a manual system, create a simple table to capture these details. Keep the format clear, with enough space for adding information as sales are processed.
Organize by Date
Arrange entries chronologically. This will help with tracking payments and identifying outstanding balances. Use the transaction date for proper recording and make sure it matches the invoice date to avoid confusion during reconciliation.
Define Customer Information
Record the customer’s full name or company name in a separate column. This ensures that each sale is attributed to the correct party and simplifies future reference or audits.
Finally, regularly update the journal as sales occur. This helps in maintaining an accurate record, ready for review at any time.
The cash receipts register tracks all incoming payments. Its components ensure clarity in handling financial transactions and are designed to streamline the accounting process. The key parts of this register include:
- Date of Transaction – Record the exact date when the payment is received. This helps maintain a chronological order of transactions.
- Source of Payment – Identify the payer, whether it’s a customer, client, or another source. It ensures that the funds can be matched to the correct account or customer.
- Payment Method – Indicate how the payment was made, such as cash, check, bank transfer, or credit card. This distinguishes between various types of payments and helps with reconciliation.
- Amount Received – Clearly state the total amount received. This is crucial for accurate reporting and financial analysis.
- Receipt Number – Assign a unique receipt number to each transaction for easy tracking and reference. It avoids confusion and provides a clear audit trail.
- Account to Credit – Specify which account should be credited with the payment. This ensures proper allocation of funds across the accounting system.
By ensuring all of these components are consistently recorded, a cash receipts register enhances financial accuracy and accountability. Regular review of the register also helps detect any discrepancies early on.
Ensure every sale is recorded with the correct details to avoid discrepancies. Begin by verifying the customer’s information, including the product or service sold, the quantity, and the agreed price.
Use a consistent method for entering transaction details in your sales journal. This includes:
- Product descriptions or service details
- Transaction date and invoice number
- Amount sold and payment method
- Applicable taxes, if any
Always double-check calculations, especially with taxes and discounts. Accurate entries will not only help maintain a clear record but also assist in timely reporting for financial analysis.
Consistency in the format used for recording transactions prevents errors during review and ensures transparency during audits. Additionally, aligning your sales records with your cash receipts journal makes reconciliation smoother.
Use clear, understandable terms and avoid shorthand that might confuse future reviews. With careful attention to detail, accurate record-keeping reduces the risk of errors and improves the quality of financial reporting.
Begin by creating clear categories that align with your business model. For instance, separate cash receipts based on sources such as customer payments, sales revenue, loans, or refunds. This will help maintain a streamlined financial overview and avoid confusion when processing payments.
Separate Operating and Non-Operating Receipts
Classify payments related to day-to-day business operations (sales, services) separately from non-operating income (interest, loans). This distinction makes it easier to track profitability and assess cash flow from core business activities versus external sources.
Use Specific and Descriptive Labels
Assign descriptive labels to each cash receipt category. Instead of using vague terms like “miscellaneous,” specify the purpose of the receipt (e.g., “cash sale,” “loan repayment,” or “advance payment”). This approach ensures clarity in your financial reporting and reduces the risk of misclassification.
Ensure accuracy by recording all transactions immediately. Delaying entries can lead to forgotten details, resulting in errors and incomplete records. Keep entries clear and precise to avoid confusion later. Avoid using vague descriptions that can be misinterpreted during future reviews or audits.
Another common mistake is failing to reconcile the journals with bank statements. Regular reconciliation ensures that discrepancies are caught early, preventing financial misstatements. It also helps maintain transparency in financial reporting.
Be cautious of omitting supporting documentation for entries. Every transaction should be backed up with relevant receipts, invoices, or agreements. This provides a clear trail for validation and audit purposes.
Key Mistakes and How to Fix Them
| Common Mistakes | Recommended Fix |
|---|---|
| Delaying journal entries | Record transactions as soon as they occur |
| Vague descriptions | Provide specific details and clear descriptions for each entry |
| Neglecting to reconcile | Regularly reconcile journals with bank statements and records |
| Missing supporting documents | Attach all receipts, invoices, or contracts to each journal entry |
Finally, review journal entries regularly to spot and correct mistakes early. Regular audits will also help ensure compliance with accounting standards and practices.
To reconcile sales and cash receipts entries, regularly compare recorded sales with cash deposits. Ensure all sales invoices match the cash entries in the journal. Cross-check bank statements to identify discrepancies between expected deposits and actual cash receipts.
Steps for Accurate Reconciliation
First, verify that each sales entry aligns with a corresponding cash receipt. If a receipt does not appear in the bank statement, investigate any possible delays or errors. Then, check for any unrecorded sales that may not have been entered into the journal. These could include cash sales or adjustments not yet reflected in the system.
Handling Discrepancies
If discrepancies arise, promptly adjust the journal entries. For sales not yet recorded, ensure the proper amount is added. If the deposit amounts differ, confirm that the right transaction was logged and check for errors in transaction amounts or dates.
Ensure the proper structure of your sales and cash receipts journal template by using clear categories. Start with transaction dates, followed by descriptions, amounts, and payment methods. Each entry should be concise and accurate. Use a separate column for the account debited and another for the account credited, ensuring transparency in accounting practices.
Keep your journal template simple by including only necessary columns. Avoid overcomplicating the layout with excessive fields. Regularly update the journal to reflect all incoming payments promptly. A well-maintained template allows for quick and easy reconciliation at the end of each period.
Consider implementing consistent numbering for each entry to track transactions effortlessly. You can add filters or sorting options for easier navigation. Customize the template based on your specific business needs, but make sure it stays organized and user-friendly for all team members.