A well-structured receipt of material template ensures clear documentation of incoming goods, minimizing errors and discrepancies. To create a reliable template, include fields for date, supplier details, item descriptions, quantities, and condition upon arrival. These elements provide transparency and accountability in inventory management.
Use a standardized format that accommodates various types of materials. A table layout works best, allowing easy comparison between expected and received quantities. Adding a signature field for verification strengthens internal controls and prevents disputes.
Consider integrating barcode or QR code functionality to streamline data entry. Digital versions can also link directly to procurement systems, reducing manual input errors. Whether paper-based or electronic, a structured template improves tracking and enhances operational efficiency.
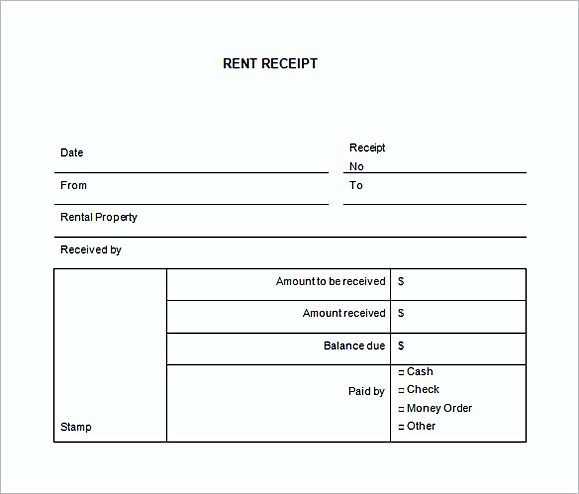
Receipt of Material Template
Use a structured template to track received materials accurately. A well-organized format ensures clear documentation and minimizes discrepancies.
- Date of Receipt: Record the exact date materials arrive to maintain precise inventory tracking.
- Supplier Information: Include the supplier’s name, contact details, and reference numbers for easy verification.
- Material Description: List item names, specifications, and quantities to match the purchase order.
- Condition Check: Note any visible damage, defects, or shortages before accepting delivery.
- Receiving Personnel: Specify the name and signature of the person verifying the materials.
- Document References: Attach purchase orders, packing slips, or invoices for complete record-keeping.
Standardizing this process improves accuracy, prevents disputes, and simplifies audits. Ensure every receipt is properly signed and stored for future reference.
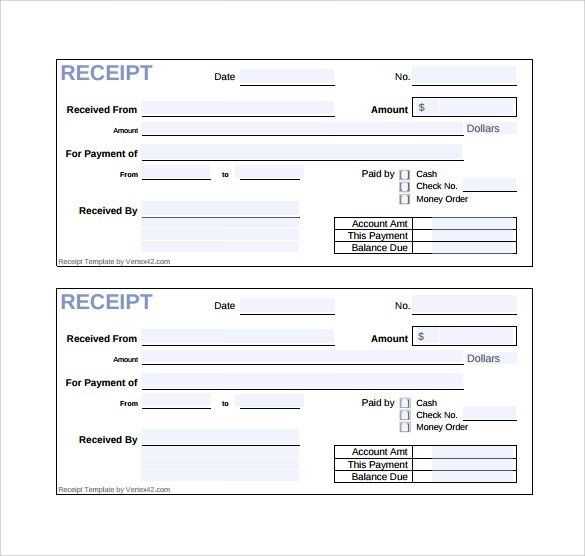
Key Data Fields in a Material Receipt Template
Ensure accuracy and consistency by including these essential fields in a material receipt template:
- Receipt Number – Assign a unique identifier to track each transaction.
- Date of Receipt – Record when the materials arrive to maintain an accurate timeline.
- Supplier Information – Capture the name, contact details, and address of the supplier for reference.
- Purchase Order Number – Link the receipt to the corresponding purchase order to verify the transaction.
- Item Description – Include product names, specifications, and unit measurements for clarity.
- Quantity Received – Log the exact number of units received to match the order.
- Unit Price – Note the agreed-upon price per unit for cost verification.
- Total Cost – Calculate the overall amount based on quantity and unit price.
- Condition of Materials – Specify if items are intact or damaged upon arrival.
- Storage Location – Indicate where materials are placed for easy retrieval.
- Authorized Signature – Require approval from the responsible party to confirm receipt.
Consistency in these fields simplifies auditing, inventory tracking, and supplier management. Ensure all details align with purchase records to prevent discrepancies.
Documenting Supplier and Shipment Details
Record the supplier’s full legal name, contact details, and business identification number to ensure accurate tracking and compliance. If the supplier uses multiple locations, specify the exact origin of the shipment.
Shipment Identification
Assign a unique reference number to each delivery for quick retrieval. Include the invoice number, purchase order reference, and any internal tracking codes.
Delivery Conditions

Document the shipping method, carrier name, and estimated arrival date. Note any special handling instructions, temperature requirements, or security measures. If delays occur, log the reason and the updated timeline.
Attach scanned copies of all supporting documents, such as packing lists, certificates of origin, and compliance statements. Keep records accessible for audits and dispute resolution.
Recording Quantities and Unit Measurements
Use consistent units to avoid errors in inventory tracking. If weight-based measurements are required, stick to kilograms or pounds instead of mixing both. The same applies to volume and length.
Define measurement units clearly
Ensure every recorded quantity includes a unit label. For example, instead of writing “50,” specify “50 kg” or “50 liters.” This prevents misinterpretation and standardizes reporting.
Maintain accuracy in data entry
Round values only when necessary, and document the exact figures when precision matters. If materials arrive in mixed units (e.g., cases and individual pieces), convert them into a single unit type for consistency.
Use automated systems whenever possible. Barcode scanners and digital records reduce manual errors and improve efficiency. If using spreadsheets, set up validation rules to prevent incorrect unit entries.
Handling Discrepancies and Damaged Goods
Check all received materials immediately. Compare the shipment contents against the packing list and purchase order. If quantities do not match or items are incorrect, document the issue with clear photos and detailed notes.
Reporting Issues
Notify the supplier and relevant internal teams without delay. Provide a concise summary of discrepancies or damage, including product codes, batch numbers, and packaging conditions. Attach photographic evidence and any supporting documents.
Returning or Resolving Discrepancies
Follow the supplier’s return policy. If a replacement is required, request confirmation of the expected delivery date. For minor discrepancies, negotiate a partial credit or discount. Update records to reflect any adjustments made.
Integrating Material Receipts with Inventory Systems

Ensure real-time data synchronization by connecting material receipts directly to your inventory system. Automate updates using barcode scanning or RFID tracking to eliminate manual input errors and prevent discrepancies.
Set up automated alerts for stock level changes. Configure notifications when received materials push inventory above or below predefined thresholds. This prevents overstocking and reduces shortages.
Standardize receipt formats to maintain consistency. Use structured templates with mandatory fields such as item codes, quantities, batch numbers, and supplier details. This improves data accuracy and accelerates processing.
Implement approval workflows to verify receipts before they impact stock records. Require supervisors to review and confirm deliveries, ensuring that only inspected and approved materials are added to inventory.
Integrate with procurement and finance to streamline tracking from purchase orders to payments. Syncing these systems ensures accurate cost allocation, prevents duplicate orders, and simplifies auditing.
Leverage reporting tools to analyze receipt patterns and supplier performance. Track delivery accuracy, lead times, and discrepancies to optimize purchasing decisions and negotiate better terms.
Compliance and Record-Keeping Requirements
Ensure all material receipts are documented accurately and consistently. All records should be organized, readily accessible, and comply with local regulations. Maintain a clear chain of custody for materials, and ensure proper documentation accompanies each item received. Records should reflect the exact quantities, condition, and source of the materials, ensuring transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain.
Document Retention and Access
Materials receipts must be retained for a minimum period specified by regulatory bodies, often ranging from 3 to 7 years. Ensure records are stored in a secure system that allows easy retrieval. Implement regular audits to verify the integrity and accuracy of the records. Access control mechanisms should restrict unauthorized personnel from altering or deleting records.
Audit Trail and Verification

An audit trail is essential for tracking and verifying receipt transactions. Each material entry should include details such as date, time, and personnel involved in the process. Verification processes should be in place to confirm that received items match the purchase order and delivery note. Discrepancies should be investigated promptly and documented.
| Document Type | Retention Period | Access Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Receipt of Materials | 3-7 years (depending on regulations) | Restricted to authorized personnel |
| Delivery Notes | 3-5 years | Accessible only with proper credentials |
| Purchase Orders | 3-7 years | Accessible to management and audit teams |