
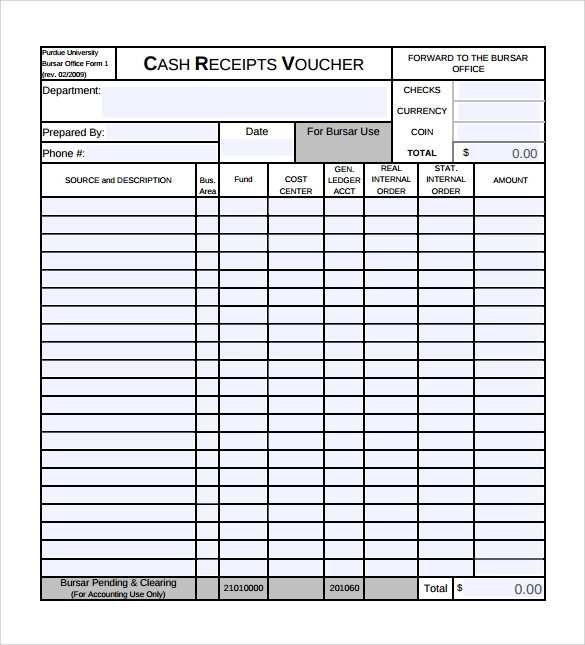
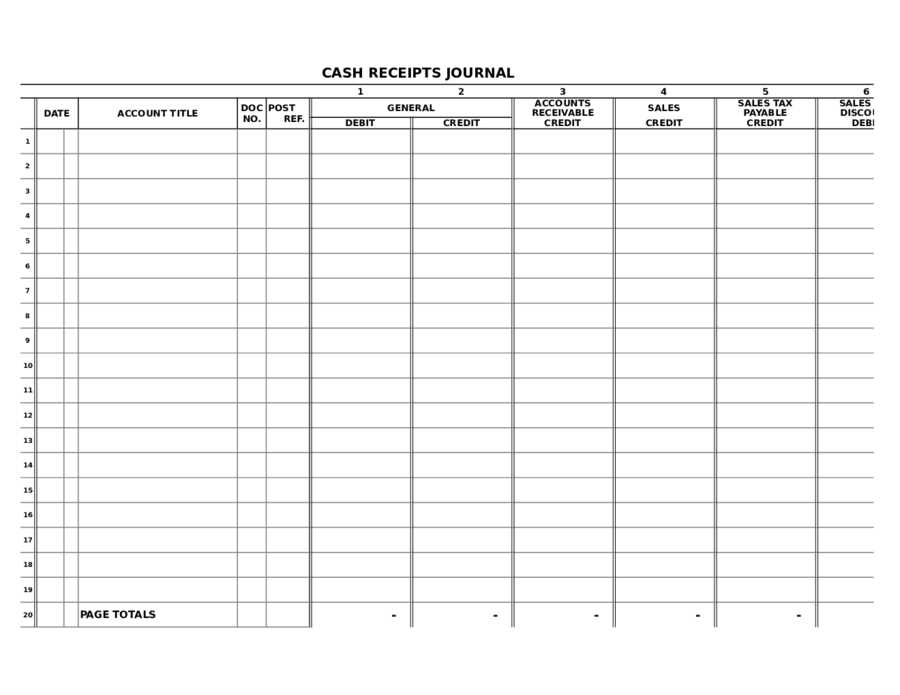
Use a structured cash receipts journal to track incoming payments accurately and maintain clear financial records. A well-designed format helps categorize transactions, identify revenue sources, and streamline bookkeeping. Keeping all receipts organized prevents errors and simplifies reporting.
Include key columns such as date, receipt number, payer name, description, payment method, and amount received. A designated section for notes allows adding details about partial payments or special conditions. Standardizing these elements ensures consistency and reduces reconciliation time.
Opt for a digital or printable template with preformatted sections for quick data entry. Spreadsheets with automated calculations improve accuracy by summing totals automatically. If using accounting software, ensure the format integrates seamlessly with your existing system.
Regularly review and update your journal to maintain accurate records. Reconcile entries with bank deposits to detect discrepancies early. A structured approach minimizes errors and supports financial transparency.
- Cash Receipts Journal Format Guide
Structure your cash receipts journal with clearly defined columns. Include the date, receipt number, payer name, description, payment method, and amount received. Organizing data this way ensures accuracy and easy tracking.
Use Consistent Categorization
Group transactions based on payment sources, such as cash, checks, or electronic transfers. Assign specific account codes to streamline bookkeeping and simplify reconciliation.
Verify Entries Regularly
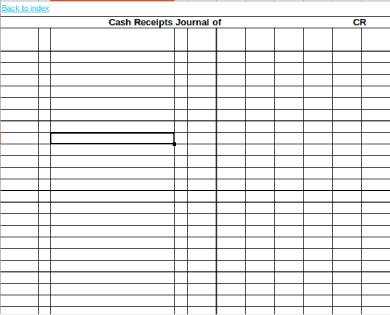
Cross-check journal entries with bank deposits and supporting documents. Identify discrepancies early to maintain accurate records and avoid errors in financial reports.
Transaction Date and Reference Number
Record the exact date of each transaction to maintain chronological accuracy. Assign a unique reference number to every entry, ensuring quick identification and tracking.
Payment Details and Amounts
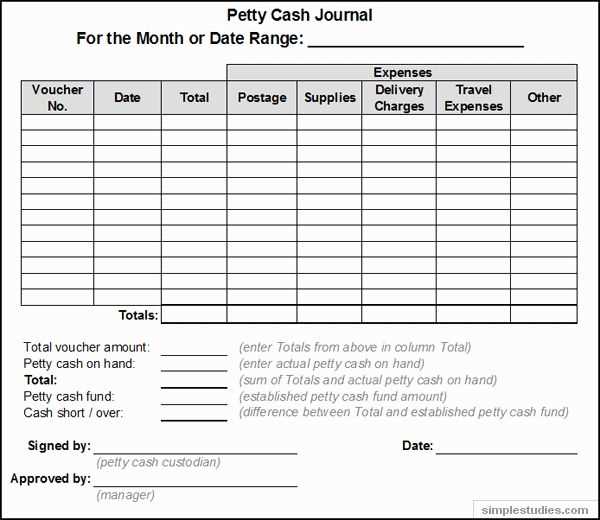
Specify the payer’s name and payment method, whether cash, check, or electronic transfer. Clearly document the amount received and allocate it to the correct account category.
Include a concise description of each transaction, linking it to invoices or sales records for transparency. Consistent formatting and clear labeling prevent misinterpretations and streamline financial reviews.
Design a cash receipts journal template with clear sections for quick entry and accuracy. Use a table format with labeled columns for date, receipt number, payer, payment method, amount, and purpose. Keep the layout uncluttered to ensure smooth data entry.
Use Consistent Formatting
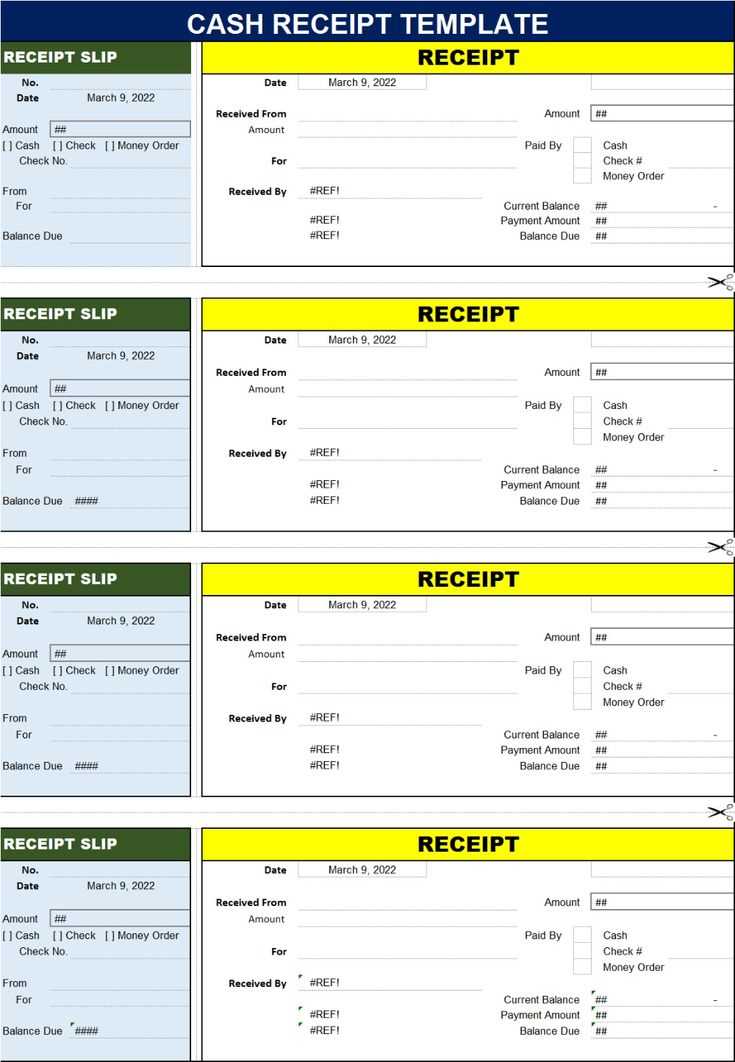
Align text and numbers properly to improve readability. Choose a uniform font and size, and apply bold headers for clarity. If using a digital format, incorporate dropdown menus for payment methods and automatic calculations for totals.
Ensure Accuracy with Validation
Prevent errors by adding built-in checks. Use formulas to verify totals and highlight discrepancies. If working with spreadsheets, lock formula cells to maintain integrity. Regularly review and update the template to align with current financial needs.
Record transactions immediately to prevent discrepancies. Delayed entries lead to errors and miscalculations, making reconciliation difficult. Use a structured format with clear categories for dates, amounts, payment methods, and descriptions to ensure accuracy.
Standardize abbreviations and terms to maintain consistency. Avoid vague descriptions–each entry should provide enough detail to identify the transaction without additional clarification. Regularly verify totals against bank statements to catch discrepancies early.
Use sequential numbering for receipts and invoices to track missing records easily. If corrections are needed, document adjustments instead of deleting entries to maintain an audit trail. Keep digital backups to safeguard data against loss or damage.
Skipping receipt details leads to discrepancies. Always include date, amount, payer, and purpose. Missing information creates gaps in records and complicates audits.
Incorrect Categorization
Misplacing transactions in the wrong accounts distorts financial reports. Use predefined categories and verify entries before finalizing.
- Check account assignments before posting.
- Review past entries for consistency.
- Train staff on proper categorization rules.
Math Errors
Manual calculations often introduce mistakes. Automate sum totals and cross-check with software-generated reports.
- Use spreadsheet formulas to avoid miscalculations.
- Reconcile totals with bank statements regularly.
- Have a second person review high-value entries.
Consistently applying these practices reduces errors, ensures accuracy, and simplifies reporting.
Adjust column headers to match transaction types specific to your business. Retail stores may need fields for sales tax and payment methods, while service providers can benefit from sections for client names and invoice numbers.
Choose between daily, weekly, or monthly layouts depending on transaction volume. High-frequency cash transactions require a detailed breakdown, whereas lower volumes work well with summarized formats.
Automate calculations by integrating formulas for totals, taxes, and discounts. Spreadsheets with built-in functions reduce errors and save time, ensuring accuracy in financial records.
Ensure compliance by incorporating necessary regulatory fields. Businesses handling multiple currencies should add exchange rate columns, while tax-exempt organizations may need documentation fields for exemption details.
Design the format to align with accounting software for easy data import. Consistent column structures and standard date formats simplify integration, reducing manual entry and reconciliation efforts.
Choose a digital cash receipts journal if speed, accuracy, and automation are priorities. Manual records require time-consuming data entry and frequent error checks, while digital solutions automate calculations and reduce human mistakes.
- Data Accuracy: Digital systems minimize miscalculations and duplicate entries. Manual methods rely on handwriting and manual input, increasing the risk of discrepancies.
- Efficiency: Digital formats allow instant search and retrieval. Paper-based records demand physical storage and take longer to review.
- Security: Cloud-based journals offer encrypted backups and user access controls. Physical copies are vulnerable to loss or damage.
- Cost: Manual tracking requires notebooks, printed forms, and storage. Digital solutions may have subscription fees but eliminate paper and printing expenses.
- Compliance: Digital systems generate audit-ready reports and integrate with tax software. Handwritten records require manual reconciliation and formatting.
For businesses handling large transaction volumes, digital solutions save time and reduce errors. If transactions are minimal, a manual system may suffice, but it lacks the convenience of automated calculations and reporting.
Organizing cash receipts efficiently requires a structured journal format. A well-designed table streamlines data entry, making it easier to track transactions and maintain accuracy.
| Date | Receipt Number | Payer | Payment Method | Amount | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01/10/2025 | CR-1001 | John Doe | Credit Card | $250.00 | Consultation Fee |
| 01/11/2025 | CR-1002 | Jane Smith | Bank Transfer | $400.00 | Service Payment |
Ensure each entry includes a unique receipt number for quick reference. Categorizing payments by method simplifies reconciliation, reducing errors. Regularly reviewing entries helps identify discrepancies before they become issues.


