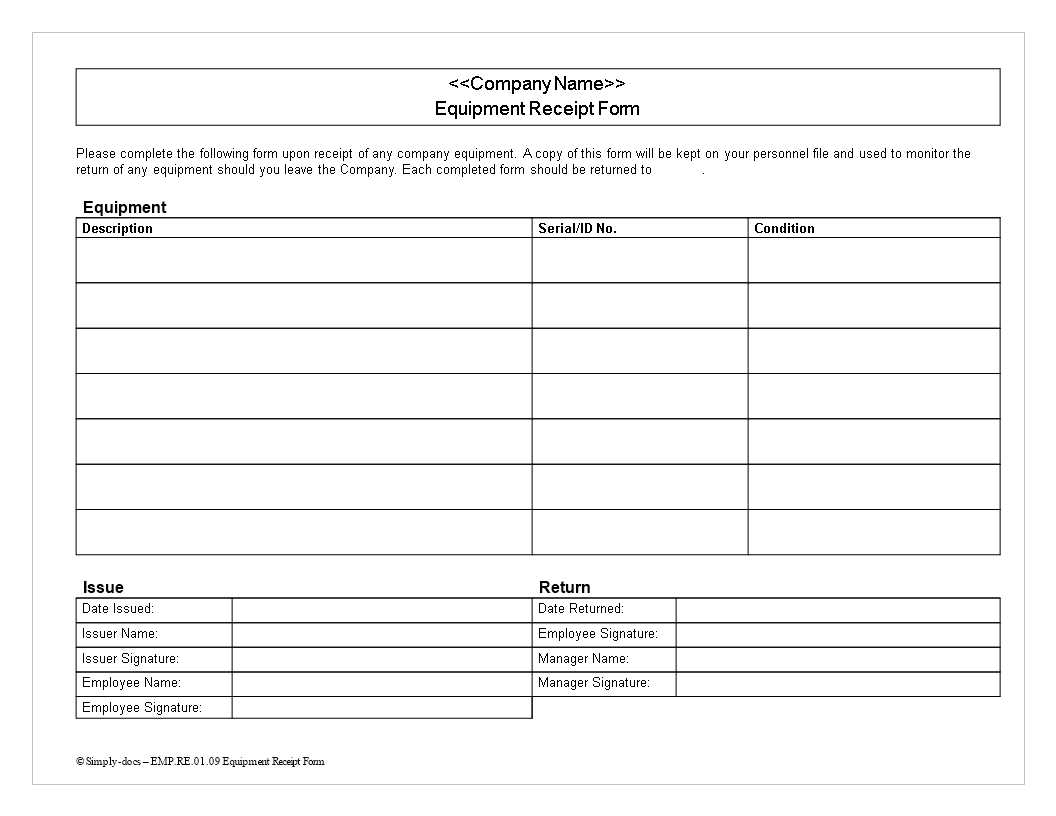
A well-structured equipment interchange receipt ensures smooth asset tracking and minimizes disputes. This document records the transfer of equipment between parties, specifying key details such as condition, time, and location. A clear format prevents misunderstandings and provides legal protection in case of discrepancies.
Include fields for equipment ID, condition assessment, timestamps, and responsible parties. Digital templates with automated entry options help reduce errors and streamline documentation. Standardized layouts improve consistency, making audits and record-keeping more efficient.
Paper-based receipts should have pre-printed sections to minimize handwriting inconsistencies, while digital versions benefit from dropdown menus and auto-fill fields. For additional security, consider requiring electronic signatures or photo documentation of equipment at the time of transfer.
Avoid missing or vague information by using a template that enforces required fields. This ensures accountability and simplifies future reference. Below, you’ll find a detailed breakdown of essential components and best practices for creating a reliable equipment interchange receipt template.
Equipment Interchange Receipt Template

A well-structured equipment interchange receipt ensures seamless tracking of assets between parties. The document should clearly state the condition, identification details, and timestamps of equipment transfers to prevent disputes and maintain accountability.
Key Elements to Include

Each receipt must feature essential details such as the equipment type, serial number, and condition upon interchange. Include fields for the date, time, and location of the transfer, as well as the names and signatures of both parties. A unique reference number helps streamline record-keeping and retrieval.
Best Practices for Accuracy
Ensure all information is entered legibly and without ambiguity. Use predefined condition codes to standardize reporting and minimize misinterpretations. Digital templates with automated input validation can further reduce errors and improve efficiency.
Regularly review and update your template to align with operational needs and regulatory requirements. Consistency in documentation strengthens asset management and enhances trust between involved parties.
Key Data Fields to Include in an Equipment Interchange Receipt
Include the following fields to ensure a complete and accurate equipment interchange receipt:
1. Identification Details
Record the unique identifiers of both parties involved. This includes the carrier’s name, the equipment provider’s name, and any reference numbers such as the Bill of Lading (BOL) or interchange control number.
Specify the equipment type (e.g., chassis, container, trailer) and its identification number. If applicable, include the VIN, license plate number, or ISO code.
2. Condition and Timestamp
Document the exact date and time of the interchange. Use a standardized format (e.g., YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM) to avoid confusion.
Detail the equipment’s condition at the time of transfer. Note any pre-existing damages with descriptions and, if possible, attach supporting images or inspection reports. If repairs are needed before use, include a remark.
3. Location and Signatures
Specify the location of the interchange, including the terminal, depot, or yard name. GPS coordinates or a specific dock number can enhance accuracy.
Ensure both parties sign the receipt. This can be a physical signature or a digital acknowledgment, depending on the system used. A clear record of authorization prevents disputes.
These fields create a structured, verifiable receipt, reducing errors and disputes while maintaining compliance with logistics standards.
Formatting and Layout Guidelines for Clear Documentation
Use a structured layout with consistent spacing, font sizes, and alignment. Keep margins uniform to ensure readability, and limit font variations to one or two styles.
Use Tables for Structured Data
For equipment interchange receipts, tables improve clarity by organizing information into rows and columns. Include headers like “Part Number,” “Description,” “Quantity,” and “Condition” to prevent misinterpretation.
Highlight Key Information
Make critical details stand out with bold or uppercase text, but avoid excessive styling. Use whitespace strategically to separate sections without overwhelming the reader.
Keep line spacing between 1.2x and 1.5x to improve legibility. Avoid cramming too much text into a single section–break up content with bullet points where necessary.
Consistently apply date and number formats. If using a 24-hour time format, maintain it throughout. The same applies to currency symbols, units of measurement, and abbreviations.
Review the layout before finalizing to catch inconsistencies or misaligned elements. A clear, well-structured receipt reduces errors and speeds up processing.
Compliance and Record-Keeping Considerations for Interchange Receipts

Store interchange receipts for at least five years to meet audit and legal requirements. Digital copies should be backed up in secure, encrypted storage. Paper records must be kept in climate-controlled environments to prevent deterioration.
Mandatory Information on Interchange Receipts

- Transaction date and time
- Names of parties involved
- Vehicle or equipment identification number
- Condition report with supporting photos
- Signatures from both parties
Audit Readiness and Compliance
Ensure receipts are timestamped and stored in a searchable format. Use standardized templates to avoid missing details. Conduct periodic internal audits to confirm compliance with industry and regulatory standards.
For companies handling high volumes, implement automated data entry and retrieval systems. This reduces errors and speeds up verification processes during audits or disputes.
Failing to maintain proper records can result in fines, legal liability, and operational disruptions. Keep records organized and easily accessible to avoid compliance issues.