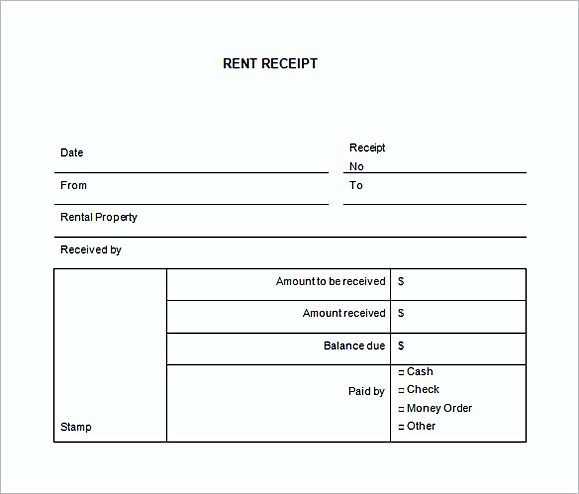
Need a structured and customizable medical receipt? An XLS template simplifies the process, ensuring accurate records and seamless financial tracking. Instead of manual entries or generic receipts, a well-designed spreadsheet automates calculations and organizes essential details.
Why use an XLS template? It allows quick input of patient information, services rendered, costs, taxes, and payment details. Formulas handle calculations, reducing errors and saving time. Plus, the format is adaptable–modify fields, add branding, or integrate with other records.
For best results, include standard elements such as provider details, patient name, invoice number, service description, and total amount. Conditional formatting can highlight overdue payments, while drop-down menus speed up data entry. With the right setup, an XLS receipt template becomes a reliable tool for medical billing.
Medical Receipt Template XLS: Practical Guide

Use a structured spreadsheet format to ensure clarity and accuracy. Each column should be clearly labeled, such as Date, Patient Name, Service Description, Amount, and Payment Status. This prevents errors and simplifies record-keeping.
Customizing for Your Needs
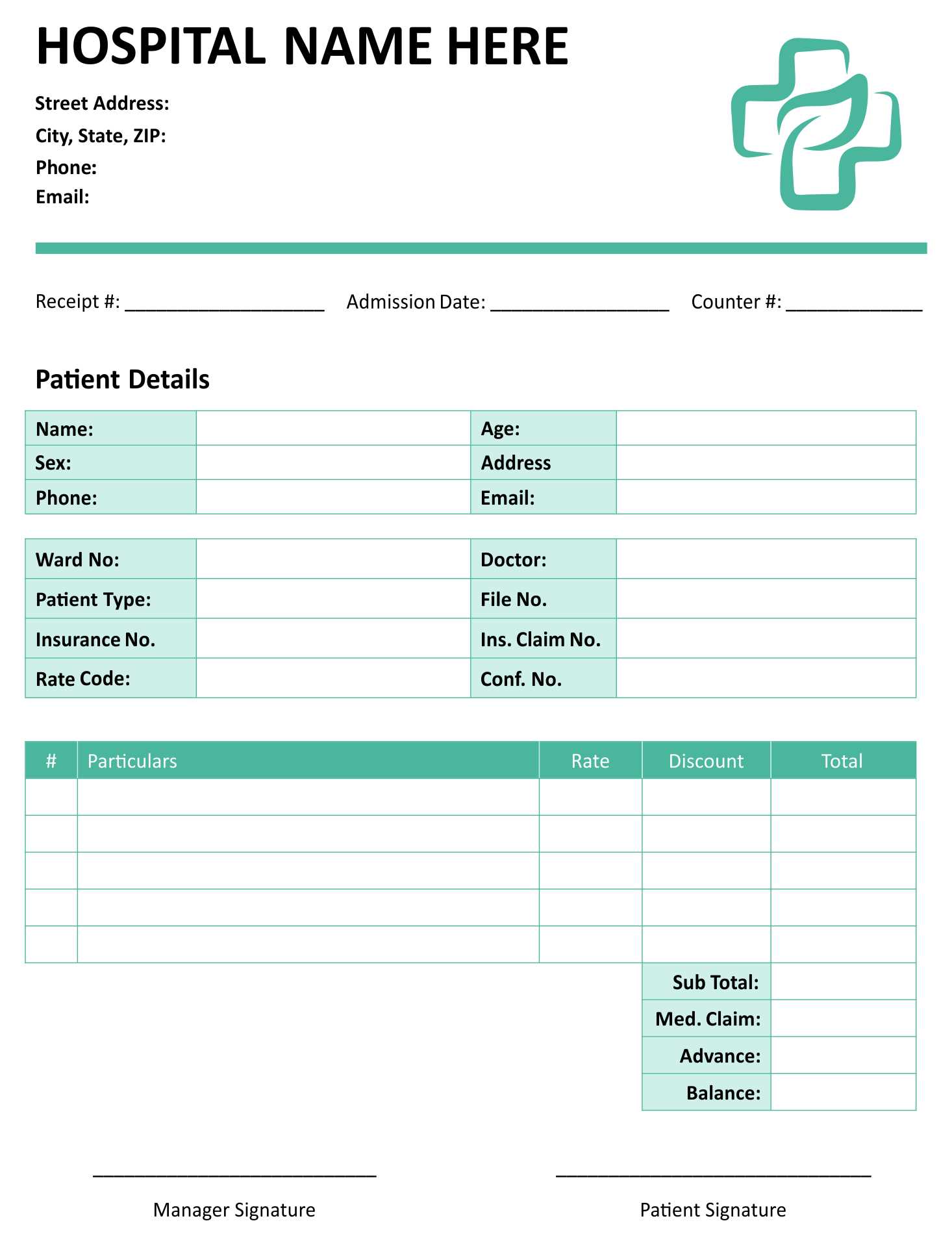
Adjust the template based on your practice’s workflow. If you frequently bill insurance, include a column for Insurance Details. For cash payments, add a section for Transaction Method. Conditional formatting can highlight unpaid invoices, making follow-ups easier.
Automating Calculations
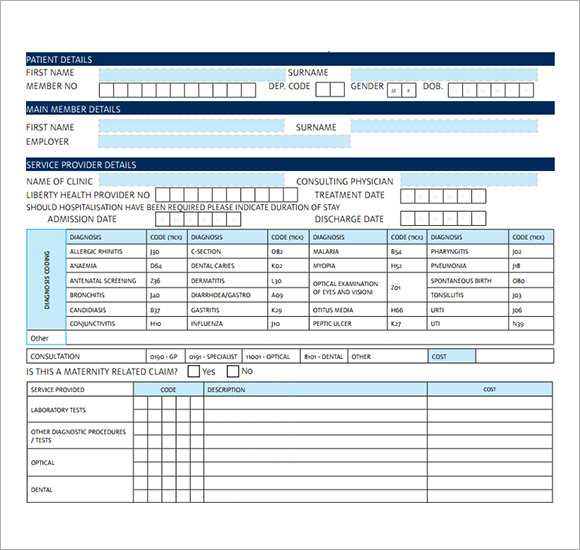
Use formulas to streamline calculations. A simple =SUM(range) formula in the Total Amount column ensures accuracy. Apply =IF statements to flag overdue payments, reducing manual checks.
Keep a master template with predefined formulas and formatting to save time. Regularly update it based on feedback from your team to maintain efficiency.
How to Structure a Medical Receipt in XLS Format

Use separate columns for date, receipt number, patient name, services provided, cost, tax, and total amount. Keep column names clear and concise to ensure easy filtering and sorting.
Format the date column as “MM/DD/YYYY” to maintain consistency. Assign a unique receipt number to each entry using an auto-increment formula. Use drop-down lists for common services to minimize errors.
Apply a currency format to cost, tax, and total amount columns. Calculate totals using =SUM() and apply a tax formula like =C2*0.08 if needed. Lock formulas to prevent accidental edits.
Use conditional formatting to highlight overdue payments. Apply filters to allow quick searches by patient name or date. Protect the worksheet to prevent unauthorized changes.
Customizing Formulas for Automated Calculations
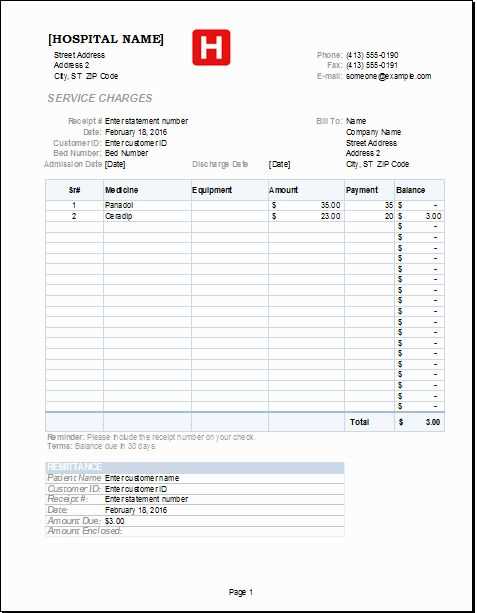
Ensure accuracy and efficiency by tailoring formulas to match specific requirements. Modify default functions or create custom ones to automate calculations and minimize errors.
- Reference Cells Dynamically: Use absolute ($A$1) or relative (A1) references to control how formulas adjust when copied across rows and columns.
- Combine Multiple Functions: Nest functions like IF, VLOOKUP, and SUMIF to handle complex conditions and calculations.
- Use Named Ranges: Assign names to key data points for easier readability and maintenance. Instead of =SUM(A2:A100), use =SUM(SalesTotal).
- Automate Date and Time Calculations: Functions like NOW() and TODAY() update timestamps automatically, while DATEDIF() calculates differences between dates.
- Prevent Errors with Logical Checks: Wrap formulas in IFERROR() to display a custom message instead of an error code.
- Optimize Performance: Avoid volatile functions like INDIRECT() when dealing with large datasets, as they recalculate frequently and slow down processing.
Test formulas thoroughly before applying them across large datasets. Adjust functions based on evolving requirements to maintain accuracy and usability.
Ensuring Compliance with Medical Billing Standards
Verify that all patient records include complete and accurate details before processing claims. Missing information leads to denials and delays.
Standardize billing codes by cross-checking entries against the latest updates in ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS. Incorrect codes result in rejected claims and revenue loss.
Maintain a clear audit trail by documenting every modification in billing records. Use automated tracking to ensure transparency and accountability.
Train staff regularly on policy changes and fraud prevention. Frequent errors can trigger compliance audits and penalties.
| Requirement | Compliance Measure |
|---|---|
| ICD-10 Code Accuracy | Verify with updated code sets before submission |
| Claim Documentation | Ensure patient details match supporting records |
| Audit Readiness | Maintain detailed transaction logs |
| Staff Training | Conduct quarterly compliance reviews |
Use automated validation tools to detect errors before submission. Early corrections reduce the risk of claim rejections and payment delays.