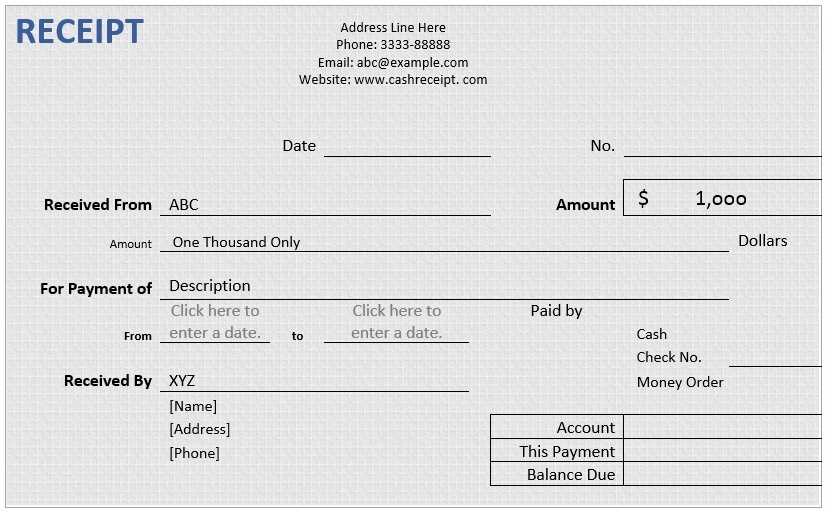
Ensure your receipt includes key details such as the donor’s name, donation date, amount, and organization information. Without these elements, the receipt may not meet tax requirements.
Nonprofits and businesses issuing tax-deductible receipts must clearly state that no goods or services were exchanged for the donation, unless partial benefits were received. In that case, the receipt should specify the value of those benefits.
Consistency in formatting helps maintain compliance and simplifies record-keeping. A standardized template should feature clear headings, organized sections, and legally required disclaimers to prevent audit issues.
Digital and printed receipts should follow the same structure, ensuring that recipients can use them easily for tax filing. Adding a unique receipt number can also help with tracking and verification.
Tax Deductible Receipt Template: Key Elements and Practical Guidelines

Include the issuing organization’s full legal name, address, and contact details. This ensures credibility and compliance with legal requirements.
Mandatory Information
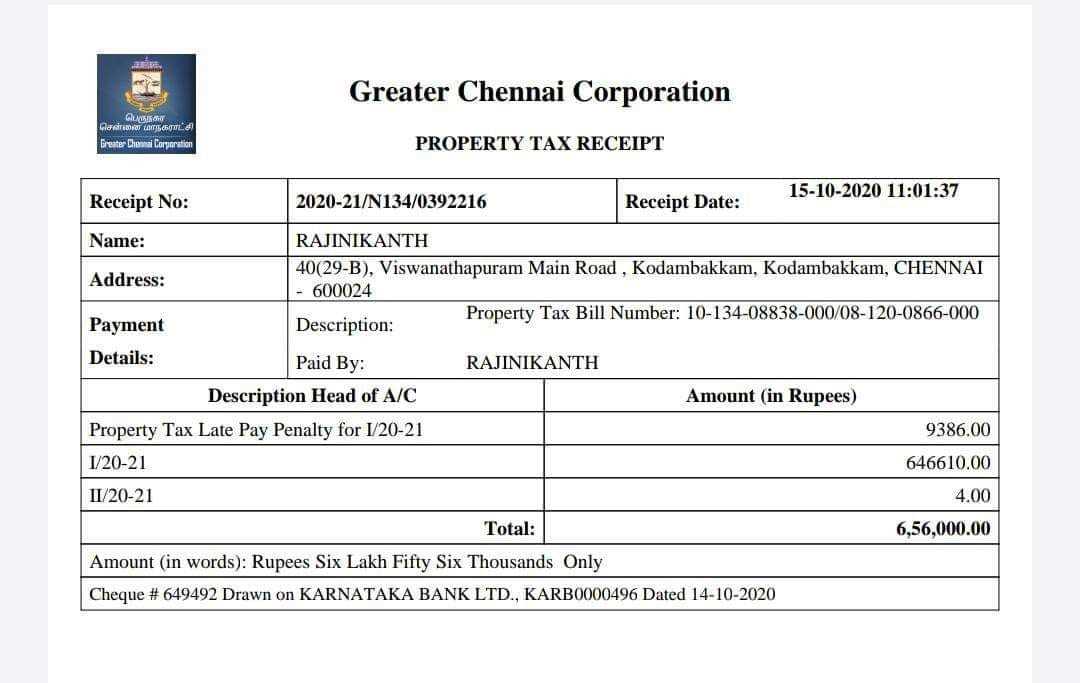
Specify the donor’s name, donation date, and the exact amount or value of the contribution. If the donation was non-monetary, describe the item in detail without assigning a dollar value unless appraised.
Add a statement confirming that no goods or services were provided in exchange, or detail any benefits received, such as event tickets, along with their estimated value.
Formatting and Storage

Use a clear, professional layout with easily readable fonts. Digital receipts should be in PDF format to prevent modifications. Maintain copies for at least five years to comply with potential audits.
Verify that the receipt aligns with tax regulations specific to your region, as requirements may vary. When in doubt, consult a tax professional to ensure full compliance.
Mandatory Information to Include in a Tax Deductible Receipt
Ensure every tax-deductible receipt contains specific details to meet legal requirements and facilitate smooth processing. Missing key elements can render the document invalid.
- Organization’s Name and Address: Clearly state the full legal name and physical address of the entity issuing the receipt.
- Date of Contribution: Indicate when the donation was made, not when the receipt was issued.
- Donor’s Name: Include the full name of the individual or business making the contribution.
- Amount or Description: For cash donations, specify the exact amount. For non-cash contributions, provide a detailed description without assigning a value.
- Statement of No Goods or Services: Confirm whether the donor received anything in return. If applicable, state the estimated value of any benefits received.
- Tax-Exempt Status: Mention the organization’s tax-exempt classification, typically referencing the relevant tax code section.
- Receipt Issuer’s Signature: While not always required, a signature from an authorized representative adds credibility.
Following these guidelines ensures compliance and simplifies tax reporting for donors.
Formatting Guidelines for Clear and Valid Documentation
Ensure all receipts include the payer’s full name, the organization’s legal name, and a valid transaction date. Avoid abbreviations that could cause confusion.
Consistent Structure
Use a standardized layout with clearly defined sections for itemized details, payment method, and total amount. Align text properly to improve readability and prevent misinterpretation.
Legible and Durable Print
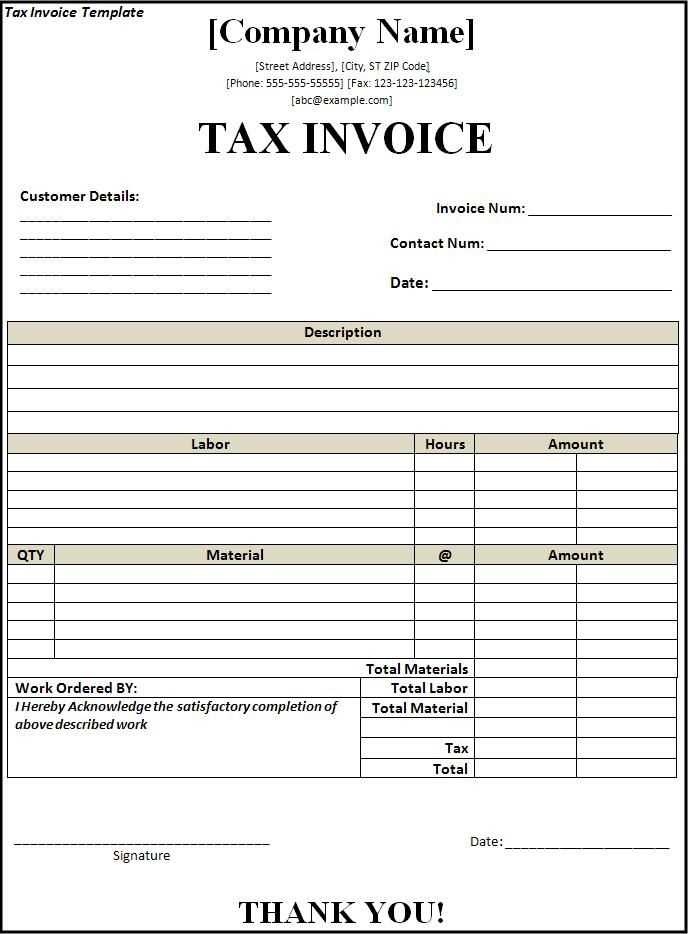
Choose a font size that remains readable when printed or scanned. Use high-quality ink or digital formats that do not fade over time. Digital receipts should be in a universally accessible format like PDF.
Double-check all entries for accuracy before issuing the document. Errors or missing details may result in rejection during audits.
Common Errors That May Invalidate a Receipt
Missing essential details makes a receipt unusable. Ensure the document includes the payer’s name, transaction date, amount, payment method, and a clear description of the goods or services provided.
Illegible or altered text raises concerns. Printed receipts should have sharp, readable fonts, while handwritten ones must be clear and without corrections that appear suspicious.
Incorrect tax information can lead to rejection. The receipt must display the correct tax amount, applicable rate, and any necessary registration numbers if required by law.
Lack of a unique identifier creates confusion. Every receipt should have a reference number to track and verify transactions easily.
Unverified signatures or missing business details weaken credibility. If a receipt requires authorization, ensure it is signed by an authorized party and includes the issuer’s full name, address, and contact information.
Incomplete breakdowns cause issues. Listing only a total amount without itemizing charges, discounts, or taxes may fail compliance checks.
Using non-standard formats or abbreviations can lead to misinterpretation. Ensure clarity by following widely accepted receipt structures and avoiding unclear shorthand.
Ignoring digital requirements leads to invalidation. If submitting electronic copies, verify that scanned or digital receipts meet format and storage regulations.