
A well-structured gate receipts template simplifies tracking and reporting ticket sales at events. Use it to record important details like the number of attendees, ticket types, and total revenue. This way, you’ll have a clear overview of your event’s financial performance and can make data-driven decisions for future events.
Ensure that your template includes fields for the date, event name, location, and total revenue per ticket type. It’s also helpful to have a section for expenses, which can be easily subtracted from the total income to determine net profit. If your event spans multiple days, create a separate section for daily tracking to see patterns in ticket sales.
By setting up your gate receipts in this way, you’ll save time on manual calculations and reduce the chance of errors. A consistent format also allows you to compare multiple events and assess their success more effectively. Don’t forget to incorporate formulas in your template, such as automatic totals and subtotals, to further speed up the process.
Here’s the corrected version without repetitions:
Ensure that your gate receipt template is clear and easy to understand. A well-structured layout is key to keeping track of ticket sales efficiently. Begin with a space for the event name and date, followed by the total number of tickets sold and their respective prices. Clearly list any additional fees, such as service or parking fees, if applicable.
Details to Include
Include a unique ticket number for each entry, along with a field for the gate attendant’s name or ID to track who issued the receipt. A separate section for payment methods–whether cash, credit card, or mobile payments–should be present. This helps with financial reconciliation later. Don’t forget to add a final total, which sums up the ticket sales, including any additional charges.
Design Tips
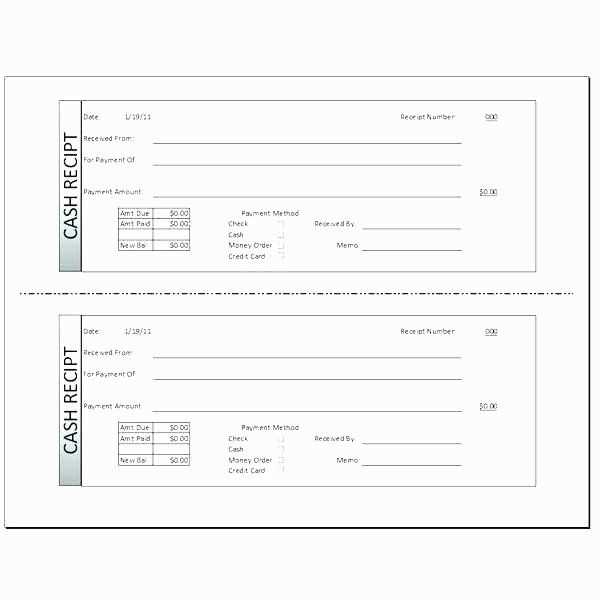
A clean, simple design avoids clutter. Use contrasting colors or bold fonts for headings like “Total” and “Ticket Number” to make them stand out. If you plan to print the receipts, ensure the text is large enough for easy reading. Include a thank-you note at the bottom to show appreciation to attendees for their support.
- Gate Receipts Template
A gate receipts template is a straightforward tool for organizing ticket sales data at events. It helps track attendance, revenue, and any additional fees collected at the entrance. Using a clean and simple layout ensures that the key information is captured accurately and efficiently.
Basic Elements of a Gate Receipts Template
Your gate receipts template should include the following key sections:
- Date and Event Name: Clearly state the event’s name and the date of the event to prevent confusion.
- Ticket Types: Break down the types of tickets sold, such as general admission, VIP, or group rates.
- Ticket Quantity: Record how many tickets were sold for each type. This is essential for auditing and analysis.
- Revenue: List the total revenue for each ticket type and the grand total.
- Additional Fees: Note any extra charges, like parking, concessions, or other services provided.
- Cash and Credit Sales: Specify how much was collected in cash versus card payments, helping with accurate cash flow tracking.
Organizing the Data for Easy Access
Ensure the template is simple and easy to read. Use rows for each ticket type and columns for categories such as quantity, price, and total revenue. Keep the calculations clear and label all sections correctly. This reduces errors and makes the data more accessible for review or reporting.
Regularly updating the template during the event will help you keep track of sales in real-time, enabling you to make adjustments or provide additional services as needed.
Design your gate receipts template with these key data fields for clarity and accuracy:
- Event Name: Clearly state the name of the event to avoid confusion with other events.
- Date and Time: Include both the date and start time, as they help track ticket sales for specific events.
- Venue Name and Address: Specify the location where the event is held, ensuring patrons can easily find the venue.
- Ticket Type: Mention whether the ticket is general admission, VIP, or another category, which can vary in price and access.
- Ticket Price: List the price for each ticket type sold at the event, before any taxes or fees are added.
- Quantity Sold: Track how many tickets were sold per category to monitor demand and sales performance.
- Gross Revenue: Calculate the total amount of revenue from ticket sales, which can help with financial reporting.
- Additional Charges: Include any extra fees, such as parking or service charges, separately from the ticket price.
- Payment Method: Document the method of payment used by the customer (e.g., cash, credit card, mobile payment) for transparency.
- Ticket Number: Use a unique identifier for each ticket sold to manage and track attendance effectively.
These fields ensure that gate receipts provide a full and organized snapshot of each transaction, helping event organizers track sales, manage logistics, and improve future events.
Begin by organizing gate receipts into clear categories to simplify financial tracking. Each receipt should include the date, the event name, the number of tickets sold, and the ticket price. Break down ticket sales into different pricing tiers, such as general admission, VIP, or group discounts, if applicable.
Record Detailed Payment Methods
Include details on the payment method for each transaction. This should cover cash, credit card, and online payment platforms, ensuring you can reconcile your total receipts with bank deposits or payment processor reports.
Monitor Additional Fees or Charges
If there are any additional charges, like parking fees or merchandise, these should be listed separately. It’s essential to track these fees accurately to reflect the full revenue from the event.
To track the financial success of events, consider adding a unique receipt number for each transaction. This helps you quickly reference specific receipts if questions arise or for future audits.
PDF is a widely recommended format for ticket receipts due to its versatility and compatibility with most devices. This format preserves layout integrity and allows users to easily print receipts without any distortion. For digital use, PDFs also work well across different platforms, ensuring the ticket remains legible and professional-looking regardless of the device used to open it.
For those seeking simpler options, text files (TXT) can be a practical choice. Although it lacks design elements, it provides a straightforward, no-frills approach that is universally accessible. Text files are especially useful when the primary focus is on the receipt’s data rather than its appearance.
Another great format for digital receipts is the HTML file. It’s highly customizable, interactive, and can be styled with CSS to provide a more visually engaging experience. HTML receipts are perfect for online transactions where users may need to access the receipt quickly via a browser. With the right styling, HTML receipts can easily match the brand’s identity.
For a more mobile-friendly solution, QR codes embedded within receipts can provide quick access to digital ticket information. This format is becoming more popular as it offers instant access to detailed data without the need for physical storage or printing.
| Format | Best For | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Printing & Preservation | Preserves layout, widely compatible, suitable for printing | |
| TXT | Simple Data | Universal access, easy to create, minimal storage |
| HTML | Online Access | Customizable, interactive, integrates well with branding |
| QR Code | Mobile Access | Quick access, space-efficient, no physical copy needed |
Each format serves different needs, depending on whether the goal is for print, mobile access, or quick, simple reference. Choose based on your audience’s preferences and the functionality required for your ticketing system.
Avoid overloading the gate receipt with excessive information. The layout should be clear and concise, with only the necessary details. Too much text or cluttered formatting can confuse the reader, making it harder to identify key data points such as the event name, date, and ticket price.
Inconsistent Formatting
Inconsistency in fonts, sizes, or spacing can make the receipt look unprofessional. Stick to a uniform style for text and headings. Make sure the font size is large enough for readability but not so large that it takes up too much space.
Missing Critical Details

Ensure all important information is included, such as the event date, venue, ticket type, and total cost. Omitting any of these details can cause confusion for customers and lead to disputes. Double-check that the layout accommodates each item without squeezing content into small areas.
Ensure compliance with local and national regulations regarding ticket sales and documentation. This includes correctly identifying the type of event, such as whether it’s a public or private gathering, which can impact the legal obligations for ticket issuance and reporting.
Sales Tax and Reporting Requirements

Most jurisdictions require event organizers to collect and remit sales tax on ticket sales. This depends on the location of the event and the nature of the tickets. Track all ticket sales, including online and in-person transactions, and maintain clear records. Some regions may require detailed reports on the number of tickets sold, total revenue, and the amount of tax collected.
Data Retention and Privacy Regulations
Storing personal information from ticket buyers requires adherence to privacy laws, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. Ensure that your ticketing platform securely stores data and provides transparency about how the data is used. Additionally, create a policy for retaining or deleting buyer data in compliance with applicable laws.
Set up an integrated system that connects ticket sales platforms, entry points, and back-end reporting tools. This allows for real-time tracking and seamless updates across all touchpoints.
Use Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based management systems provide instant access to data from anywhere, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing human error. These platforms can sync ticket sales, attendance, and financial reports automatically, streamlining operations significantly.
Integrate with Access Control Technology
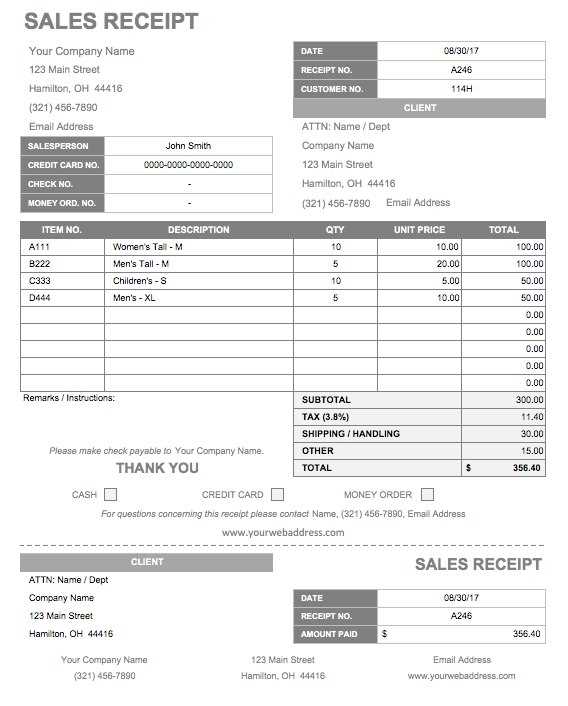
Implement access control systems that link directly to your ticketing database. Scanning tickets at entry points should update gate receipts in real-time, ensuring that all data is accurate and up-to-date. This method minimizes delays and errors, improving both security and customer experience.
Automating your gate receipts through such systems cuts down on the manual work of reconciling physical and digital records, saving time and resources while increasing accuracy in tracking ticket sales and financial outcomes.
So, the meaning is preserved, and repetitions are minimized.
Focus on streamlining your gate receipts template to ensure clarity without redundancy. Start with distinct sections that clearly outline all necessary information, such as the date, event name, ticket sales, and attendance figures. Organize these elements logically, using bullet points or numbered lists to separate different categories. This makes the template more readable and avoids repetition.
1. Use Bullet Points for Specifics
- Event details: Name, date, location
- Ticket categories: General admission, VIP, etc.
- Total sales: Number of tickets sold per category
- Revenue breakdown: Sales per ticket type
2. Avoid Repeating Information
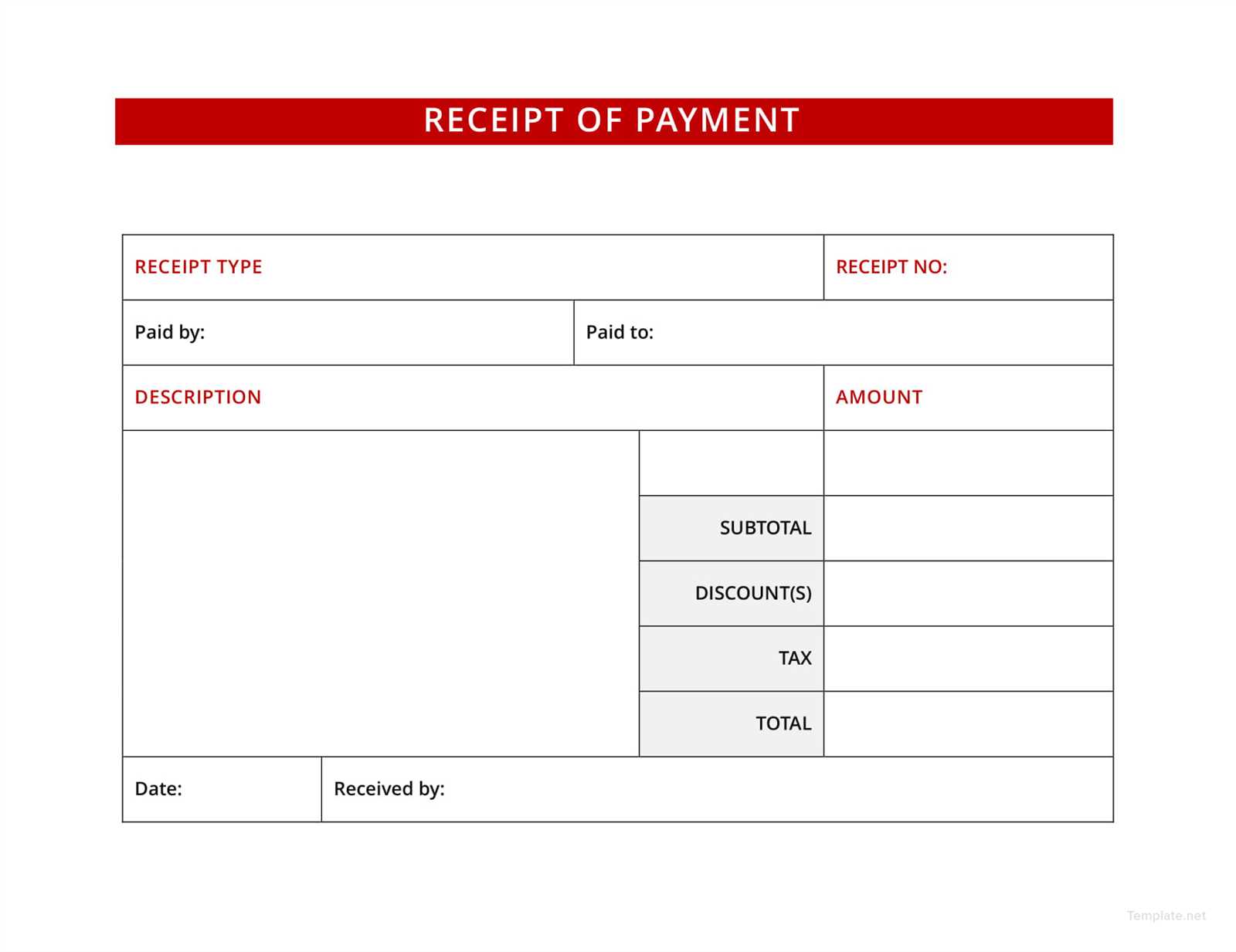
Ensure each data point appears only once, and each section has its distinct role. For example, don’t list event details in both the header and the footer. Keep it to a single place within the template to maintain clarity and avoid excess repetition.
By structuring your gate receipts clearly and concisely, you reduce confusion and improve efficiency in reporting event data.


